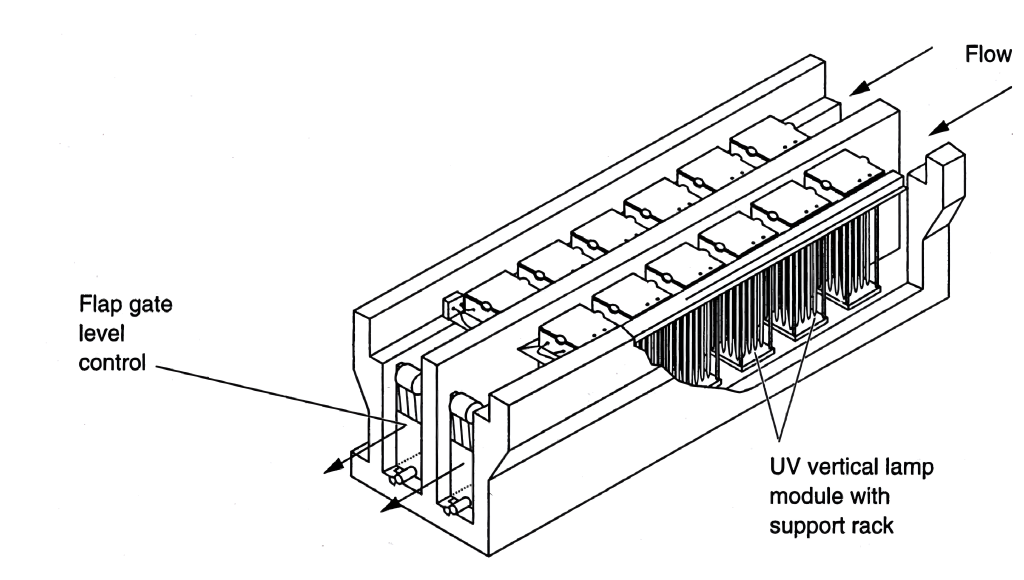
5.3.2 Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a natural component of sunlight and can also be generated through special light bulbs. UV disinfection systems accomplish microbial inactivation through damage to one or more critical biomolecules by photochemical reactions. Artificially generated UV light is commonly used for disinfection treatment in large-scale systems with high flow rates.
Some typical design parameters for these systems are shown in the following table.
| Design Parameter | Typical Design Value |
|---|---|
| UV dosage | 20 – 140 mW-s/cm2 |
| Contact time | 6 – 40 s |
| UV intensity | 3 – 12 mW-s/cm2 |
| Wastewater UV transmittance | 50 – 70% |
| Wastewater velocity | 0.05 – 0.38 m/s |
UV is effective when effluent turbidity remains low. UV lamps have a limited life and will experience reduced output over time. This will result in reduced pathogen inactivation if the system is not properly sized. Another major operational problem is the fouling of the sleeve or lamp from materials in the flow stream.
Natural UV disinfection is practiced more frequently in developing countries using shallow ponds or polishing ponds, or free-water surface flow constructed wetlands. These structures are to be designed with depths shallow enough to allow sunlight to penetrate throughout and disinfect the total depth of the water column. Direct contact with sunlight without the interference of e.g. plants in the case of vegetated wetlands or trees in the surrounding that cause shadow is essential.
The table presented below outlines the benefits and limitations of UV radiation disinfection.
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Effective inactivation of most viruses, bacteria, and protozoa | Low dosages may not effectively inactivate some viruses, spores, and cysts |
| Physical process rather than a chemical disinfectant | Turbidity and total suspended solids in effluent can render UV disinfection ineffective |
| No residual effect that could harm humans or aquatic life | May require a large number of lamps |
| Equipment requires less space than other methods | High energy demand in the case of artificial systems as well as high investment costs |
| Short contact time under respected design parameters |
